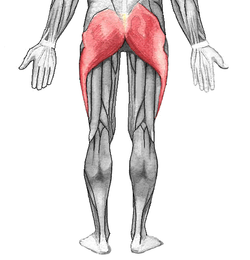
Anatomy
| Origin | Lateroposterior surface of sacrum and coccyx, gluteal surface of ilium (behind posterior gluteal line), thoracolumbar fascia, Sacrotuberous ligament |
| Insertion | Iliotibial tract, gluteal tuberosity of femur |
| Action | Hip joint: Thigh extension, thigh external rotation, thigh abduction (superior part), thigh adduction (inferior part) |
| Innervation | Inferior gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2) |
| Blood supply | Inferior gluteal and superior gluteal arteries |

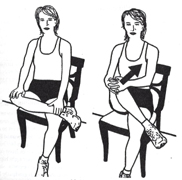
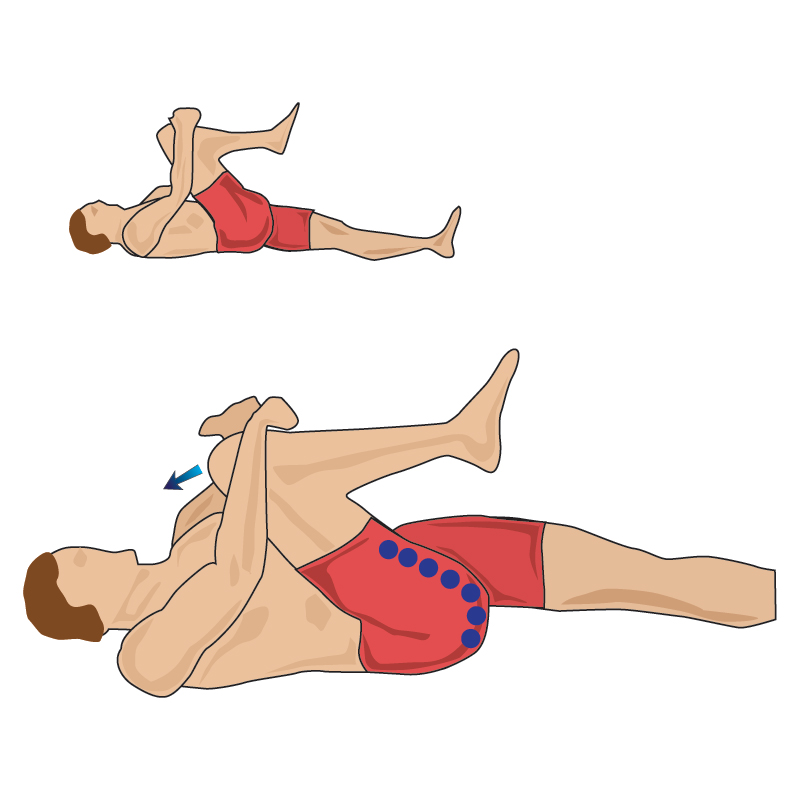
Stretching
Orthopedic Test
Gluteus Maximus Strength Test
Testing for: strength of the gluteus maximus
Procedure:
- Patient is prone
- The Patient’s knee on the affected side is flexed 90°
- Therapist stabilizes the affected hip with one hand
- Patient extends the affected hip and holds the hip/leg in extension
- If patient can hold their hip in extension against gravity, it indicates Grade 3 on the strength scale
- Therapist tries to put a downward pressure as the patient tries to hold their affecte hip in extension
- Patient can resist the therapist pressure indicates Grade 5 strength
Ober’s Test
Assessing For: the length of the Iliotibial band and Tensor Fascia Lata
Procedure:
- Patient is sidelying close to the edge of the table on the unaffected leg. Therapist stands behind the Patient.
- Flex hip and knee of the unaffected leg that is at the bottom
- Stabilize the Patient’s pelvis with one hand
- With the other hand grasping the medial aspect of the patient’s affected knee, passively hyperabduct and extend the affected femur at the hip.
- Allow the affected leg to lower without rotating
Positive Sign: the affected leg stays abducted and does not lower.