Piriformis syndrome is a condition in which the piriformis muscle, located in the buttock region, spasms and causes buttock pain. The piriformis muscle can also irritate the nearby sciatic nerve and cause pain, numbness and tingling along the back of the leg and into the foot (sciatic).
Thus by stretching and massaging the piriformis muscle, the pressure on the sciatic nerve can be reduced.
Anatomy

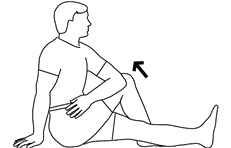
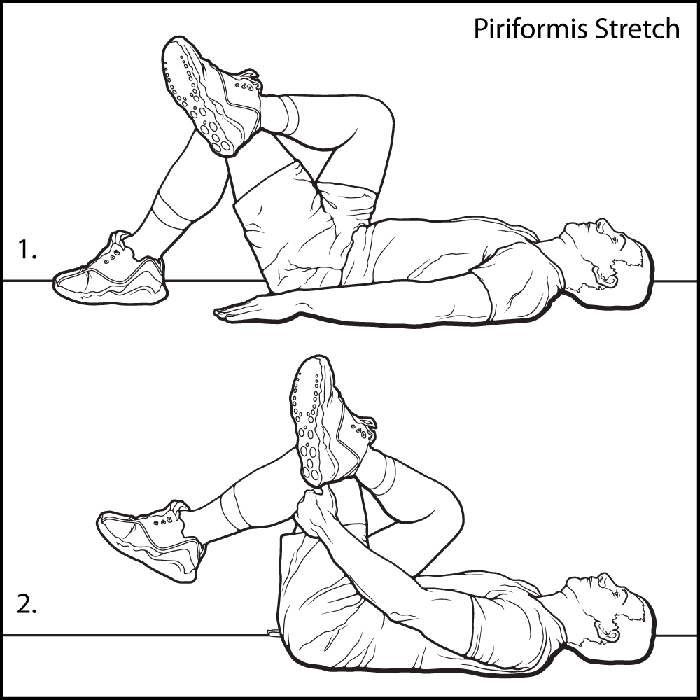
Stretching
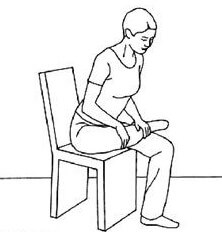
Orthopedic Tests
The Piriformis test can be performed in two methods: Piriformis test in side-lying position: For performing the test, the patient is positioned in side-lying on the unaffected side. The symptomatic leg is positioned in 60 to 90 degrees of flexion in the hip and 90 degrees flexion in the knee joint.
Pace Abduction Test
Testing for: the strength of the piriformis muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is seated, with their hips flexed 90 ° and their knees together
- Therapist places both hands on the lateral side of the knees , holding them together
- Patient attempts to move their knees apart while the therapist resists
Positive Sign: piriformis weakness if the patient cannot move their knees apart. Pain is present in the area of the piriformis indicates piriformis trigger points
Piriformis Length Test
Assessing For: the length of the piriformis muscle
Procedure:
- Patient is prone with their knees close together
- Patient flexes both their knees to 90°
- Slowly separate the lower legs away from the midline, while keeping the knees together (the internal rotation of the femur stretches both piriformis muscles)
- The normal internal rotation would be (45°-50°) from the midline
Positive Sign: short piriformis muscle is indicated if the internal rotation is less than 45°